Raised blood sugar levels are a complication of poorly managed diabetes. We use the term “hyperglycemia” to describe this condition (high blood sugar). Damage to the body’s microcirculation might result from chronically elevated blood sugar levels. Just think about what would happen to sugar if it were left out in the open for an entire night. This turns sticky. It’s easy to see how sugar “clings” to your tiny blood capillaries and impedes blood flow to your organs now.
Most often, blood vessel damage shows up in the kidneys, liver, feet, eyes, and brain. This article will investigate the reasons for this injury. The heart, eyes, and kidneys are among the vital organs that diabetes can harm. When diabetes isn’t taken care of well, it can lead to a number of serious comorbidities, which are diseases that happen along with diabetes but aren’t related to it. People with type 1 and type 2 diabetes need to find the right treatment plan to avoid these problems.
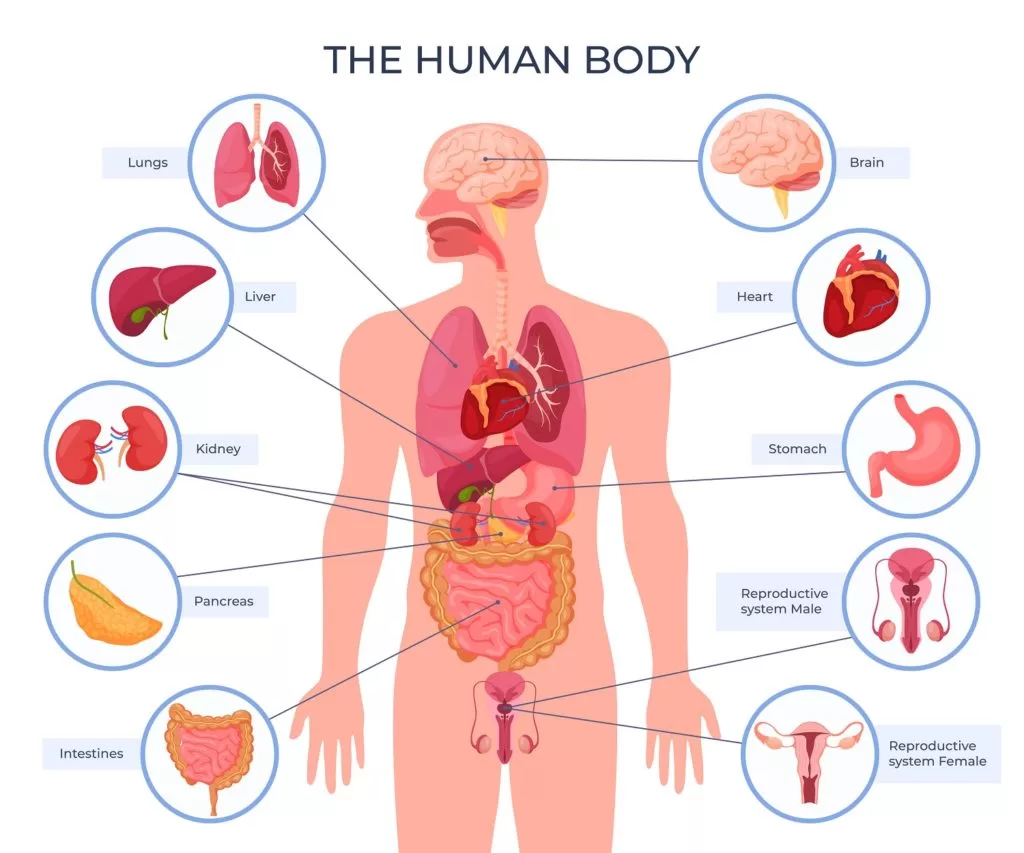
So let’s take a look at which organs are affected by high blood sugar levels so that you can be aware of any negative effects from the potential dangers of this issue. Please read the following without bias or regard for the severity of the dangers to the organ in question. We chose it at random.
1. Heart
Hearts are an element of the circulatory system. The blood arteries are a part of this system as well, and they are responsible for delivering oxygen and nutrients to the body’s organs and tissues. In addition to carrying oxygen and nutrients to your cells, your blood arteries also get rid of harmful gases and waste products.
The American Heart Association (AHACVD) says that diabetes is one of the seven main risk factors for cardiovascular disease that can be avoided. Heart disease, stroke, and other circulatory system disorders are collectively classified as CVDs.
The main cause of this disease is the buildup of plaque, which is made of cholesterol, on the walls of the arteries. Diabetes can cause problems with platelets, which help the blood clot. This makes the patient more likely to get CAD. Plaques can cause diabetes and are more likely to break off and obstruct blood flow.
According to research, people with high blood sugar have a higher risk of developing cardiovascular disease than the general population. Diabetes could cause damage to the blood vessels and nerves that control the heart over time. The risk of cardiovascular disease increases in proportion to the duration of diabetes.
There is a strong correlation between having diabetes and having another illness that raises the risk of heart disease, such as:
- Disorders of the cardiovascular system
- Poor lipid profile
- Triglyceride levels that are too high
2. Brain
Thinking and remembering might be negatively impacted by high blood sugar. According to the available research, the neuroanatomical make-up of the brain is also known to be affected by diabetes. The result is a 50% higher risk of developing dementia in people with diabetes compared to those without the disease.
Research shows that diabetics have reduced gray matter density and volume in some brain regions. Most of the brain and spinal cord are composed of gray matter. It’s important for normal life and how we do things. Loss of gray matter density and volume can have big effects on the health of the brain and nerves.
The brain’s tiny blood vessels are equally vulnerable to the ravages of diabetes. This can cause brain tissue death or a stroke.
3. Kidneys
The kidneys, which are bean-shaped, are situated in the abdominal cavity, below the rib cage, and on each side of the spine. They’re each about the size of a closed fist. They are a component of the kidney’s larger system, which also includes:
- A person’s ureters are the tubes that carry urine from their kidneys to their bladder.
- Urine is held in the bladder until it is released.
- Excretion occurs via the urethra.
As a filtering organ, the kidneys play an important role in the body. They are responsible for getting rid of toxins, excess fluid, and acid from the body. Maintaining a proper concentration of blood plasma salts and minerals requires healthy kidneys.
Vitamin D and erythropoietin are also made in the kidneys. Vitamin D is essential for calcium absorption and for maintaining a robust immune system. The hormone erythropoietin encourages the body to make more red blood cells.
High blood sugar is linked to chronic kidney disease. High blood sugar can potentially damage the blood vessels that are inside the kidneys. Because of this, waste and fluid can build up in the blood, making it less able to clean the body of toxins. Diabetic nephropathy is the medical term for this condition.
Untreated diabetic nephropathy can progress to renal failure, which can be fatal. About 18% of adults who have diabetes also have advanced chronic kidney disease, according to the CDC.
4. Pancreas
A dysfunctional pancreas has been linked to diabetes. Your pancreas is responsible for making insulin, which explains why this occurs. The inability or incapacity of the pancreas to generate insulin can lead to hyperglycemia.
This defect in insulin synthesis results in type 1 diabetes. Insulin resistance, on the other hand, is what causes type 2 diabetes. The pancreas struggles to keep up with the increased demand for insulin.
Diabetes can either directly or indirectly lead to pancreatic cancer. Pancreatic cancer is more common in people with type 2 diabetes, and diabetes can be a complication of pancreatic cancer.
5. Gut and Stomach
The vagus nerve is susceptible to injury from high blood sugar levels. Here we see the nerve that travels all the way from the base of the brain to the lower half of the body. Gastroparesis is a manifestation that is brought on by injury to the vagus nerve.
Your stomach discharges food far more slowly than it should when you have this illness. This could result in issues like:
- Dehydration
- Gastroesophageal reflux disease, often known as stomach acid in the food pipe (GERD)
- Unexpected fluctuations in blood sugar levels
- Malnutrition caused by improper food digestion
People with diabetes are more likely to suffer from gastroparesis (20–50%).
6. Teeth and Mouth
The glucose in your saliva is a good indicator of this. When a diabetic person spits, there is a lot of glucose in their saliva, which helps dangerous microorganisms grow. grow. Plaque is a thin film that forms on teeth and gums when bacteria and food interact. Cavities and tooth decay can be caused by certain forms of plaque. Other people are the root of bad breath and gum disease.
Diabetes can make the effects of gum disease worse, and it may take longer to get better. To make things even worse, gum disease can make it hard to keep your blood sugar at a healthy level.
Plaque can harden into tartar over time, making it harder to remove with a toothbrush and floss. Gums may become inflamed, red, and bleed easily when this occurs. These symptoms are indicative of gingivitis, a disease of the gums.
If gingivitis isn’t treated, it can lead to periodontitis, which is a more serious form of gum disease. Gum recession causes the formation of pockets between the teeth and gums. The virus spreads to these spots and may linger there for a long period of time.
If left untreated, periodontitis can harm the gums, bones, and tissues that hold teeth in place. Your teeth could grow loose, requiring extraction.
7. Lungs
Negative effects on pulmonary function may result from uncontrolled diabetes. This may result in minor side effects like asthma or serious side effects like lung fibrosis.
Scientists are still unsure what causes breathing difficulties in diabetics. Inflammation has been hypothesized to play a role in this.
Drugs used to treat hypoglycemia have been linked in certain studies to an increased risk of lung disease in diabetics. One discovered that different drugs may have different effects on the lungs. Hypotheses have been made that the diabetes drug Glucophage (metformin) can help treat lung disease, while insulin may make it worse.
8. Eyes
Diabetic eye symptoms, such as blurred vision, may appear first in some people. Diabetic retinopathy develops over time as a complication of diabetes. Problems with eyesight or complete blindness may result from this disorder.
High blood sugar levels can severely damage the retina and blood vessels of the eyes. That light-sensitive layer of tissue at the back of your eye is called the retina. When there are problems with the blood vessels, the body tries to fix them by making new blood vessels that are weaker and more likely to bleed.
Retinal swelling caused by diabetes is called diabetic macular edema and is caused by blood and fluid leakage from new, thinner blood vessels. As a result, the macula (the retina’s central area) swells.
Neovascular glaucoma is a type of secondary glaucoma that happens when blood vessels grow and then seal over the part of the eye where the cornea and iris meet. The cornea is the transparent layer that covers the eye’s front. It’s the iris, the colored component of your eye.
Diabetes patients experiencing eyesight loss should get prompt medical attention. Although treatment may not restore normal vision, it may prevent further loss of sight.
9. Sexual Organs
If something goes wrong with the circulatory system, blood flow will go down. Damage to the nerves and their ability to send signals can also cut off blood flow to the penis, so be careful of this. Men with diabetes may experience erection problems as a result of this.
Your body’s capacity to process glucose is also essential to the health of your sperm. Poor sperm health is a potential side effect of diabetes, which impairs this ability. It’s possible that mature sperm are less mobile and unable to fertilize an egg.
Diabetes can affect fertility in both males and females. Men with diabetes may experience diminished amounts of the male hormone testosterone. As a result, sperm count and sexual desire may decrease.
Vaginal dryness is another potential side effect of diabetes in women, as is nerve l, is another risk factor. Lack of blood supply to the uterus and ovaries is another possible outcome of blood vessel loss in females.
Insulin aids in the production of hormones that keep reproductive tissues healthy and control ovulation in women who don’t have diabetes. This procedure will be less effective for someone who has diabetes.
Polycystic ovarian syndrome and diabetes have both been associated with insulin resistance (PCOS). High quantities of the male hormone testosterone lead to this disease. Because of this, conceiving is a challenge.
10. Skin Complications due to blood Sugar
Treatment and Prevention High blood sugar can lead to impaired circulation, which can lead to skin complications. Because of this, your skin may be harmed, and your body may have more difficult time healing wounds.
Skin problems can happen to anyone, but people with diabetes are more likely to get a few specific ones. For example, one sign of diabetic dermopathy is small, round, brown spots on the lower legs. About 55 percent of those who have diabetes will eventually go blind.
In the early stages of necrosis lipoidica diabeticorum, red bumps show up on the lower legs. After progressing to this stage, the lesions develop a smooth, flat top and can be any shade of yellow or brown. One percent or less of diabetics will eventually experience this complication.
Diabetes can cause blisters that look like burn blisters, but they are not painful like burn blisters are. They often form groups. Eruptive xanthomatosis manifests itself on the skin as raised, yellow, and red pimples.
Diabetics frequently suffer from foot sores. They might be minor or severe and manifest on the big toes and the balls of the feet. Their seriousness is often ranked from 0 to 5. For example, a score of 0 means that the lesion may have healed, while a score of 5 means that gangrene has set in, which means that the tissue has died.
Conclusion:
Having diabetes that isn’t under control raises the likelihood that you’ll experience a number of complications. The heart, blood vessels, kidneys, lungs, pancreas, digestive system, and brain are just some of the key organs and systems that may be impacted by these issues. The mouth, teeth, eyes, skin, and genitalia can all suffer damage from high blood sugar levels.
Diseases including heart disease, pancreatic cancer, and kidney failure are all made more likely by having diabetes. The best approach to preventing these dangerous conditions is to keep your blood sugar under control.
Disclaimer:
The author’s views are his or her own. The facts and opinions in the article have been taken from various articles and commentaries available in the online media and Eastside Writers does not take any responsibility or obligation for them.
Note: Contact our Writers at www.eastsidewriters.com for writing Blogs/Articles on any niche. We have experts in various domains from Technology to Finance and from Spirituality to Lifestyle and Entertainment.







Pingback: Avoid Letting Chronic Stress Control Your Life- It Can Be Dangerous
Pingback: The Power of Pomegranate -This Superfood Can Help You Lose Weight - Eastside Writers